By: Omar García y Karim Senior
Topic: Cancer and Stem cell.
Objective:Understand applications of stem cells on cacer.
Cancer is a term used for disease in which abnormal cells divide without control and are able to invide other tissue .Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body the blood and lymph system. The stem cells fight against bad cells (cancer cells) and replace them.
1. What is cancer ?
Cancer is not just one disease but many diseases. There are more than 100 different types of cancer. Most cancers are named for the organ or type of cell in which they start - for example, cancer that begins in the colon is called colon cancer; cancer that begins in basal cell of the skin is called basal cell carcinoma.
Cancer types can be grouped into broader categories. The main categories of cancer include:
- Carcinoma - cancer that begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs.
- Sarcoma - cancer that begins in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue.
- Leukemia - cancer that starts in blood-forming tissue such as the bone marrow and causes large numbers of abnormal blood cells to be produced and enter the blood.
- Lymphoma and myeloma - cancers that begin in the cells of the immune system.
- Central nervous system cancers - cancers that begin in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
Sometimes, this onderly process goes wrong.New cells from when the body does not need them,and old cells do not die when they should.These extra cells can form a mass of tissue called TUMOR or GROWTH.
 |
| This is a cancer cell (this show how cancer cell growth with) |
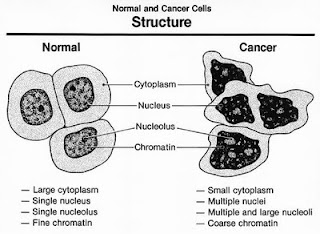 | |
| The structure of a normal cell and cancer cell. |
What are the causes of cancer ?
Research shows that certain risk factors increase the chance that a person will develop cancer.
These are:
- Growing older
- Tobacco
- Sunlight
- Ionizing Radation
- Certain chemicals and other substances
- Some viruses and bacteria
- Certain hormones
- Family history of cancer
- Alcohol
- Poor diet, lack of physical activity, or being overweight
How can cancer be preventive ?
Cancers that are closely linked to certain behaviors are the easiest to prevent:
- Choose not to smoke tabacco.
- Don´t drink alcohol.
 |
| No-Smoking-No-Drinking-No-Drugs |
- Protecting your self with a hat and shirt when in the sun,and using sunscreen!
- Stay in the shide.
 |
| Use sunscreem to protect your skin. |
- Diet
 |
| Cancer prevent food pyramid |
- Vaccinations
- Cervical cancer (many women receive a vaccination for the human papillomavirus because this virus´s is relationated with this type of cancer.)
- Liver cancer (Hepatitis B vaccines prevent hepatitis B virus, wich can cause this type of cancer).
 |
| vaccination is important. |
- Systematic Screening
the systematic screening include:
-Mammograms
-Testicular self - examination
-Breast self - examionation
-Pap smears.
These can prevent many types of cancers.

| |||
|
2. What is Stem Cells ?
It is a cell, having in it the incredible ability to replicate and make any type of cell required to build or repair anorganism. It is responsible for our growth from a single cell to a mature adult. Our bodies use stored stem cells to repair tissue damage throughout our lives. This amazing ability gives hope to stem cell therapies.
Microscopic in size, stem cells are big news in medical and science circles because they can be used to replace or even heal damaged tissues and cells in the body. They can serve as a built-in repair system for the human body, replenishing other cells as long as a person is still alive.
 |
| This is an Embryonic stem cell |
Stem cells have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the body. Serving as a sort of repair system for the body, they can theoretically divide without limit to replenish other cells as long as the person or animal is still alive. When a stem cell divides, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become another type of cell with a more specialized function, such as a muscle cell, a red blood cell, or a brain cell.
Stem cells are cells found in all multi-cellular organisms. They retain the ability to renew themselves through mitotic cell division and can differentiate into a diverse range of specialized cell types.
Types of Stem cells:
 |
| Types of stem cells |
- Totipotent-Each cell can develop into a new individual. It can produce plasenta. This mean that any totiptent has the ability to create a fetus in a woman´s uterus.
 |
| Totipotent stem cell |
- Pluripotent-Cells can form any (over 200) cell types. Capable to produce most of the tissues in the organism, they can produce any type of cell in the body but they can´t produce embryos.
 |
| Pluripotent stem cell |
- Multipotent- Cells differentiated, but can form a number of other tissues.Are those that can only generate its own layer cells embryonic origin or ancestry.They also called ¨organ-specific stem cells¨ that are capable to create a cell of a specific organ in the embryos or in an adult. One example of this cell is the once that contain the bone marrow, is capable to create all the cells types of the blood and immune system.
 |
| Multipotent stem cell |
- Unipotent-Only can make 2 types of stem cells:
-Embofilosis: Is a smooth cell taht cotain a liquid call vasiofelina that´s help the body to don´t harden when the reproduction of the stem cells.
 |
| Unipotent Stem Cell |
Research in the stem cell field grew out of findings by Canadian scientists Ernest A. McCulloch and James E. Till in the 1960s.
 |
| Left:James E Right: Ernest A. McCulloch |
How can Stem cells can be used for trarment of disease ?
- Umbinical cord stem cell : Extracting the blood of the baby´s umbinical cord.
- Acute leukemia
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)
- Chronic leukemia
- Juvenile Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (LMCJ)
- Refractory Anemia
ETC ...
- Spinal cord stem cell: Extracting the spinal cord stem cell of the hipbone (iliac crest) and then implanted back into the body days later.These transplanted stem cells have the ability to transform into multiple types of cells and can regenerate damaged tissue.
-Osteoarthritis(This Stem cell have the capability to regenerate cartilage as well as new blood vessels, improving function and reducing pain)
-Spinal cord injuries
-Multiple Sclerosis (is adisease that affect chronic neurological disorder that affects the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
-Cardio vascular diseases(specificly Aterosclerosis)
-Erectile Dysfunction(sometimes called "impotence," is the repeated inability to get and keep an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse.)
-Stroke
ETC...
 |
| Spinal cord |
- Stem cells in the arteries that nourish the pancreas via catheter.
This stem cell can use in the tratment of diseases like ;
- Diabetes Mellitus
Research and clinical applications of cultured stem cells: this includes the types of stem cells used, their characteristics, and the uses of stem cells in studying biological processes, drug development and stem cell therapy; heart disease, diabetes and Parkinson's disease are used as examples.
Stem Cells and Cancer
Stem cell therapy is currently at the frontier of biomedical research. A considerable volume of evidence indicates that cancer stem cells are responsible for the development of different types of tumors. Malignant transformation of stem cells may be due to the loss of normal asymmetric
division processes, cell fusion, microenviromental factors, generic and epigenetic mechanisms or carcinogenics already implicated in cancer development. A better understanding of these transforming events will allow more rational design of new specifi c therapeutic strategies targeting the cancer stem cell.
Data from 2007 suggest that approximately 1.4 million men and women in the U.S. population are likely to be diagnosed with cancer, and approximately 566,000 American adults are likely to die from cancer in 2008.Data collected between 1996 and 2004 indicate that the overall 5-year survival rate for cancers from all sites, relative to the expected survival from a comparable set of people without cancer, is 65.3%. However, survival and recurrence rates following diagnosis vary greatly as a function of cancer type and the stage of development at diagnosis. For example, in 2000, the relative survival rate five years following diagnosis of melanoma (skin cancer) was greater than 90%; that of cancers of the brain and nervous system was 35%. Once a cancer has metastasized (or spread to secondary sites via the blood or lymph system), however, the survival rate usually declines dramatically. For example, when melanoma is diagnosed at the localized stage, 99% of people will survive more than five years, compared to 65% of those diagnosed with melanoma that has metastasized regionally and 15% of those whose melanoma has spread to distant sites.
¨Cancer Stem Cell¨ (C.S.C)
 |
| Cancer Stem Cells |
A consensus panel convened by the American Association of Cancer Research has defined a CSC as "a cell within a tumor that possesses the capacity to self-renew and to cause the heterogeneous lineages of cancer cells that comprise the tumor." It should be noted that this definition does not indicate the source of these cells—these tumor-forming cells could hypothetically originate from stem, progenitor, or differentiated cells. As such, the terms "tumor-initiating cell" or "cancer-initiating cell" are sometimes used instead of "cancer stem cell" to avoid confusion. Tumors originate from the transformation of normal cells through the accumulation of genetic modifications, but it has not been established unequivocally that stem cells are the origin of all CSCs. The CSC hypothesis therefore does not imply that cancer is always caused by stem cells or that the potential application of stem cells to treat conditions such as heart disease or diabetes, as discussed in other chapters of this report, will result in tumor formation. Rather, tumor-initiating cells possess stem-like characteristics to a degree sufficient to warrant the comparison with stem cells; the observed experimental and clinical behaviors of metastatic cancer cells are highly reminiscent of the classical properties of stem cells.
The CSC hypothesis suggests that the malignancies associated with cancer originate from a small population of stem-like, tumor-initiating cells.
n hepatocellular carcinoma, cellular analysis suggests the presence of stem-like cells Definitive markers have yet to be identified to characterize these putative CSCs, although several potential candidates have been proposed recently. In other cancers in which CSCs have yet to be identified, researchers are beginning to link established stem-cell markers with malignant cancer cells. For instance, the proteins Nanog, nucleostemin, and musashi1, which are highly expressed in embryonic stem cells and are critical to maintaining those cells' pluripotency, are also highly expressed in malignant cervical epithelial cells. While this finding does not indicate the existence of cervical cancer CSCs, it suggests that these proteins may play roles in cervical carcinogenesis and progression.
Do CSCs Arise From Stem Cells?
Given the similarities between tumor-initiating cells and stem cells, researchers have sought to determine whether CSCs arise from stem cells, progenitor cells, or differentiated cells present in adult tissue. Of course, different malignancies may present different answers to this question.
In the previous picture:
The molecular pathways that maintain "stem-ness" in stem cells are also active in numerous cancers. This similarity has led scientists to propose that cancers may arise when some event produces a mutation in a stem cell, robbing it of the ability to regulate cell division. This figure illustrates 3 hypotheses of how a cancer stem cell may arise: (1) A stem cell undergoes a mutation, (2) A progenitor cell undergoes two or more mutations, or (3) A fully differentiated cell undergoes several mutations that drive it back to a stem-like state. In all 3 scenarios, the resultant cancer stem cell has lost the ability to regulate its own cell division.
3.Ethical implications of use ste cells.
Stem cell research is at the center of a raging controversy due to its ethical implications.
Although few debate the potential marvels that mastering stem cells could provide by way of medical advancements in the treatment and prevention of life threatening diseases, many things are being made for reaching that goal. However, for the people whose moral beliefs state that human life begins at the moment of conception, embryonic research is simply unacceptable.
This is because From the ethical point of view, it has been explained that the use of human embryonary stem cells leads to the destruction of embryos and, as it is considered that life begins in the very moment the spermatozoid joins the ovule, it would mean the extermination of a life, which is something intolerable.
4.Our position (opinions)
Omar Garcia´s opinion :
In my opinion this is something that might be done for the cure of many lifes. The development of the the human medicine is on our hands, and if we stop the progress it sure be something we regret, maybe not tomorrow but later.
In
the other hand the response of those who defend the ethical
implications is that the lives are being saved, but what about those who
die in problems that nobody cares. It's a small price to be paid to
save lives and improve the quality of life of the world.It really worth
it.
Karim Senior´s opinion:
Stem cells are incredible. If we contiunue to investigate about stem cells we can not only going to progress in medicine, we algo going to save the life of many people, Cure many diseases (the diseases that we say that is incurable) and many good things for our humanity.
Cancer that in many cases is terminal disease is possible ti cure with the stems cell, the CSC though me cancer is like a stem cell but malignan, this a desadvantaje. We can use CSC for cure cancer?, we need to invastigate and investigate, is the unique form to find a solution and finished with cancer definitly.
I think the ethical problems doesn´t metter if we have to save the life of a person. Wich is more important for you: life or die because my religion say that stem cells it doesn´t good ?. If I have to choose I choose LIVE, Live is one and if I have the treatment obviously I take the treatment regaless the ethical problems. and save my life. We have to changes our minds and see that stem cells are good for us in much of cases.
5. Bibliography:
THE END.
Karim Senior´s opinion:
Stem cells are incredible. If we contiunue to investigate about stem cells we can not only going to progress in medicine, we algo going to save the life of many people, Cure many diseases (the diseases that we say that is incurable) and many good things for our humanity.
Cancer that in many cases is terminal disease is possible ti cure with the stems cell, the CSC though me cancer is like a stem cell but malignan, this a desadvantaje. We can use CSC for cure cancer?, we need to invastigate and investigate, is the unique form to find a solution and finished with cancer definitly.
I think the ethical problems doesn´t metter if we have to save the life of a person. Wich is more important for you: life or die because my religion say that stem cells it doesn´t good ?. If I have to choose I choose LIVE, Live is one and if I have the treatment obviously I take the treatment regaless the ethical problems. and save my life. We have to changes our minds and see that stem cells are good for us in much of cases.
5. Bibliography:
THE END.




